

the argument that you pass must be a mutable. you can pass one argument to the set function. Here is the official documentation for function definition. the elements that are stored in a set can be different data types. Technically you can use mutable objects as keys, provided that they are hashable and you dont mutate them in a way that. But dictionaries (the container that stores keys and their values) are mutable. Curly brackets are used in dictionary entries, as well as key-value pairs separated by commas (,). Dictionary keys are typically immutable that is helpful because they must have a consistent hash. Lists and dictionaries are mutable strings and tuples are not. Here is a basic example of function definition: # a function to return the area of a square A dictionary is a Python container that stores unique keys to values in an ordered and mutable way. The types of all mutable values are compound types.
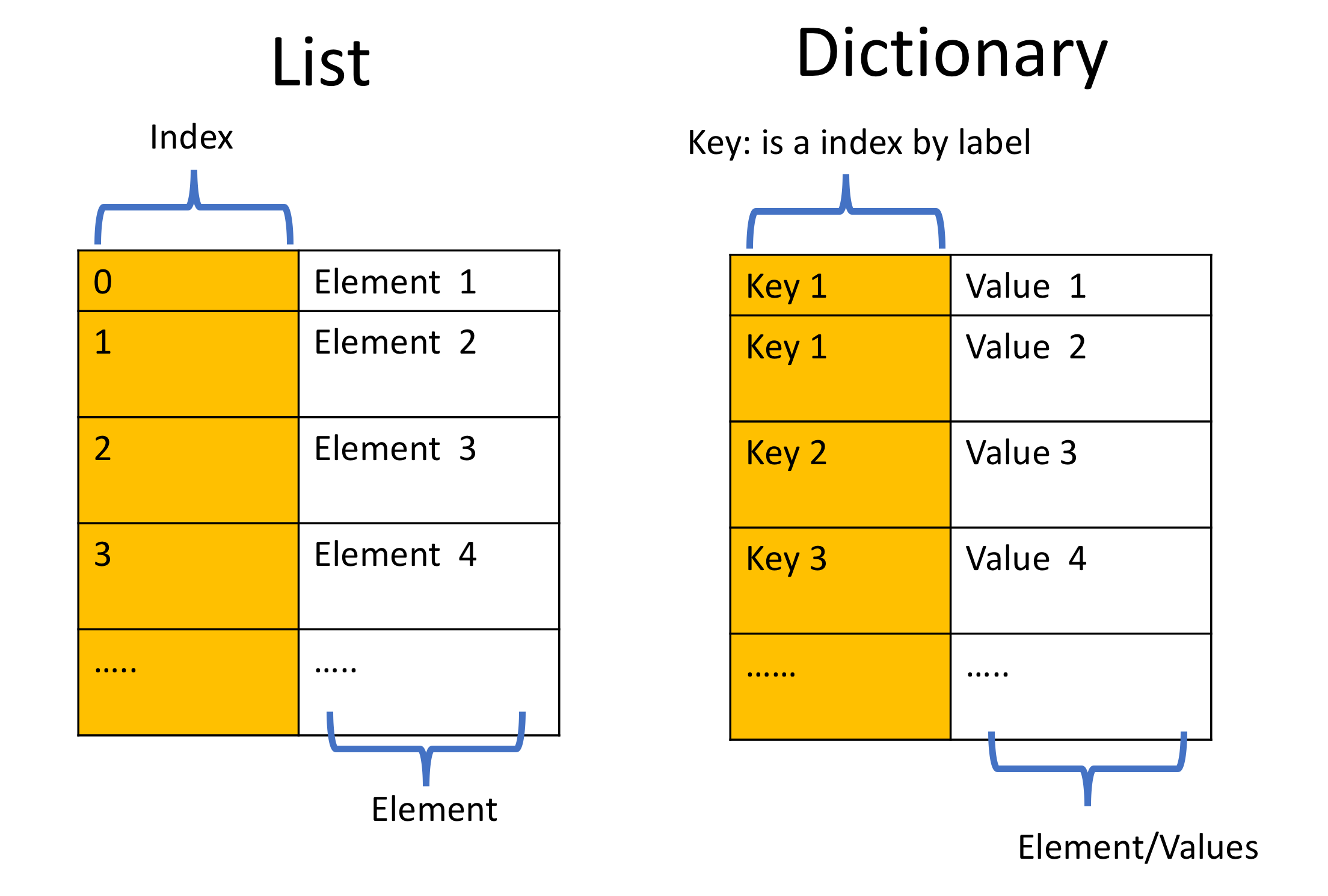
The keyword “def” followed by a list of parameters is used to define functions. Sometimes to define a funstion si useful. Here is the official documentation for dictionary and some other useful data structures. pop ( "level" ) # copy an existing dictionary into a new reference values (): print ( x ) # there are multiple ways to remove an existing entry, here is one example This leads to inefficient setting and retreiving of values, though. How do I read a dictionary key in Python Lets discuss various ways of accessing all the keys along with their. MyDict = "math" myDict = "undergrad" # looping through the keys or the values over the dictionaryįor x in myDict : print ( x ) print ( myDict ) for x in myDict. Python dictionary is a mutable data structure. MyDict = # dictionaries are mutable, thus can be modified, either modifying an existing value or creating a new key


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
